On day-21 we have seen few networking devices and terms. Now we are going to check about most imp topic in Networking which is OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model.
What is OSI?
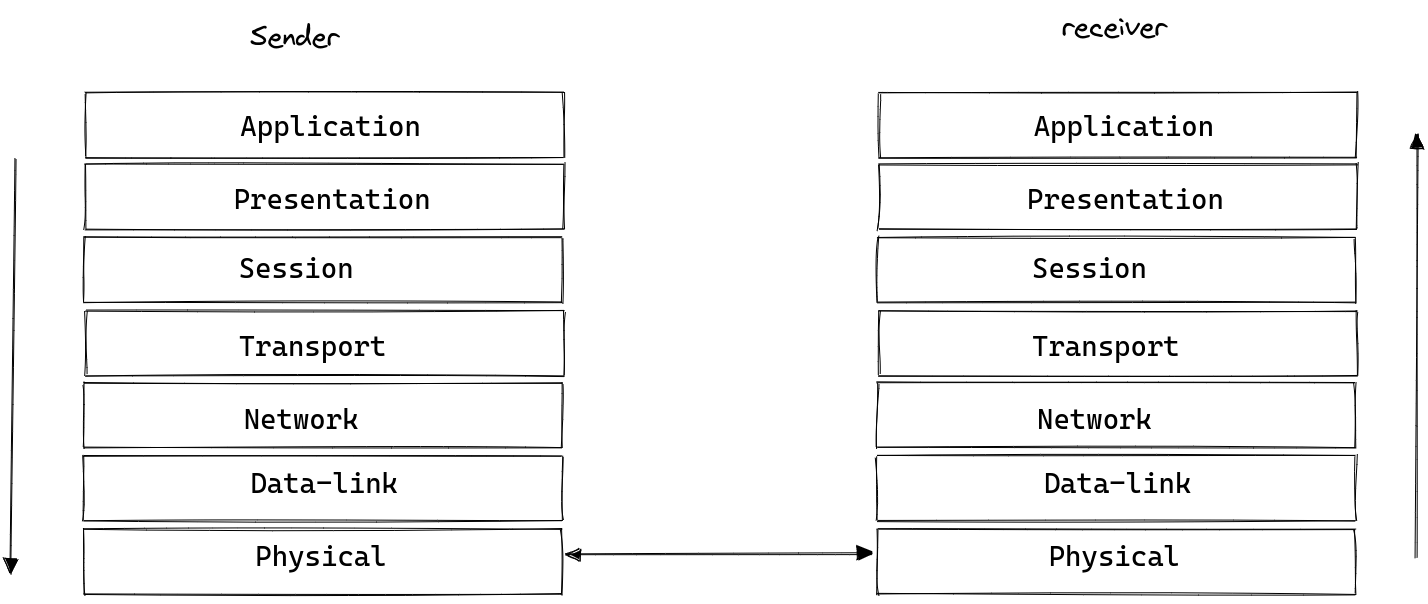
It is a standard way of representing how two network devices communicate with each other. It divides whole network communication process into 7 different layers like Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data link, Physical layer.
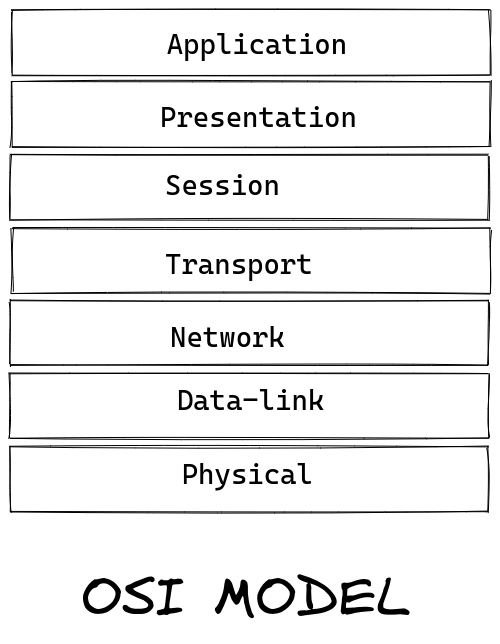
Let's look at each layer one by one.
Application Layer
As its name suggests, this layer is more connected with the application or software such as email, web browser, chat app, etc. Through application layer protocols, apps and software can send and receive data.

Let's take one example to better understand it. You want to send a e-mail to your client. You typed the mail and pressed the send button. Your data was sent to the server and the server sent it to the client email address. Here protocols like HTTP(Hyper text transfer protocol), FTP(File transfer protocol), and SMTP(Simple mail transfer protocol) are used between whole process.
Presentation Layer
The OSI model connects each layer; you send data through the application layer, but the presentation layer handles processing and converting that data into machine learning code.
Before the data movers further to other layers, a number of processes happen in this layer on data like encoding, encryption, abstraction, compression of data, etc. Like the application layer, it also has some protocols like SSL(Secure socket layer), Telnet, FTP(Server).
Session Layer
The session layer establishes sessions, or channels of communication, between devices. It is in charge of starting sessions, making sure they are active and open while data is being exchanged, and shutting them down once communication is complete. It also performs network authentication process using PAP(Password Authentication Protocol).

The session layer can also establish checkpoints during a data transmission, allowing devices to pick up where they left off in the event that the session is terminated. So sometimes you are running a data transferring process and suddenly your internet is gone, and you think you have to do the same process again but it is not like that session process will create check point and process will start again from where it was stopped.
Protocols like ASP(Apple talk session protocol), RPC(Remote Procedure Call Protocol), etc.
Transport Layer
Ok, now connection is established and data is ready to move to another layer, but who's gonna move or transport it ? The transport layer takes this responsibility and moves data to the other layer. But this process is not simple.
 First step : transport layer will divide the data into smaller chunks known as segments and assign them each sender's port no, sequence number and receiver's port number. Now sequence number is a number used when the broken data is reassembled into its original form.
First step : transport layer will divide the data into smaller chunks known as segments and assign them each sender's port no, sequence number and receiver's port number. Now sequence number is a number used when the broken data is reassembled into its original form.
Second step: Flow control which will match the receiving rate of data to its transfer rate. Third step: Error control which will checks if any packets is missing or not. If not then it will request it again.
Transport layer mainly use two protocols: TCP(Connection oriented) and UDP(Connection less)
Network layer
Now we are expanding our view and moving to other other network because the network layer is going transmit our data to the receivers network. Yeah, that's true. Network layer basically transfer our data from one network to another network.
There are two primary uses for the network layer. One method involves dividing segments into network packets and reassembling the packets at the other end.
 The other method involves finding the optimum path for packets to take across a physical network. The network layer routes packets to a destination node using network addresses, which are commonly Internet Protocol addresses.
The other method involves finding the optimum path for packets to take across a physical network. The network layer routes packets to a destination node using network addresses, which are commonly Internet Protocol addresses.
Remember router from our previous blog? The network layer uses routers to deliver packets along the desired path.
Data-Link Layer
Data link layer allows you to directly communicate with the receiver computer host. It will basically take packets from the network layer and fetches IP addresses of the sender and receiver. It breaks those packets into frames and sends them with MAC addresses of the sender and receiver.
Physical Layer
The physical layer is in charge of maintaining the wired or wireless connections between network nodes. The transmission of raw data, which is just a string of 0s and 1s, as well as bit rate control are controlled by it.
 It describes the connector, the electrical cable, or wireless technology connecting the devices.
It describes the connector, the electrical cable, or wireless technology connecting the devices.
Resources 📚
Ending notes ⛵
So, that was all for today. We looked over all the 7 layers of the OSI model and its protocols. See you on the next day with a new networking topic.


