We covered a few network protocols in the previous blog, including FTP, SMTP, HTTP, DNS, and others. Today we will look several additional network protocols, subnets and subnetting. So, let's get started.
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
As we have seen in the OSI model blog there are two network protocols available in transport layer: TCP and UDP.
TCP is connection-oriented network protocol. It means before establishing a connection it verifies the connection thoroughly. It must check whether the connection is established or not by the three-way-handshake method.
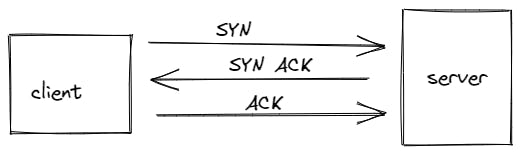
In three-way-handshake method client first send a SYN message to the server to check connection is made. Then after server sends a SYN ACK message to acknowledge previous message. At last client sends ACK message to server and with this message it confirms that connection is established perfectly.
TCP breaks down the data into segments and adds TCP header into it so that no data is missed or lost. In this header contains various things like source port, destination port, acknowledgement number, checksum, etc.
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
UDP is much similar to TCP. It also sends and receive data in transport layer but there is one difference. It is connectionless protocol which means it doesn't establish a connection and doesn't guarantee data delivery.

So, when client sends data through UDP doesn't care whether the data is received by another machine or not. It is like fire and forget.
Subnetting
In computer network every device is assigned a unique identifier which is known as IP address. This thing we already know right? There are two types of IP addresses available: IPV4 and IPV6. But for subnetting we are talking about IPV4.
Subnet means a logical subdivision of an IP network. The process of dividing a network into two or more networks is known as Subnetting. You can also say Subnet is network inside a network.
Large networks can be divided into subnets to enable IP address reallocation, which reduces traffic load and improves network efficiency. It also increases network security.
Resources
Ending Credits
So, this was all about Subnetting, TCP and UDP. See you in the next blog.


